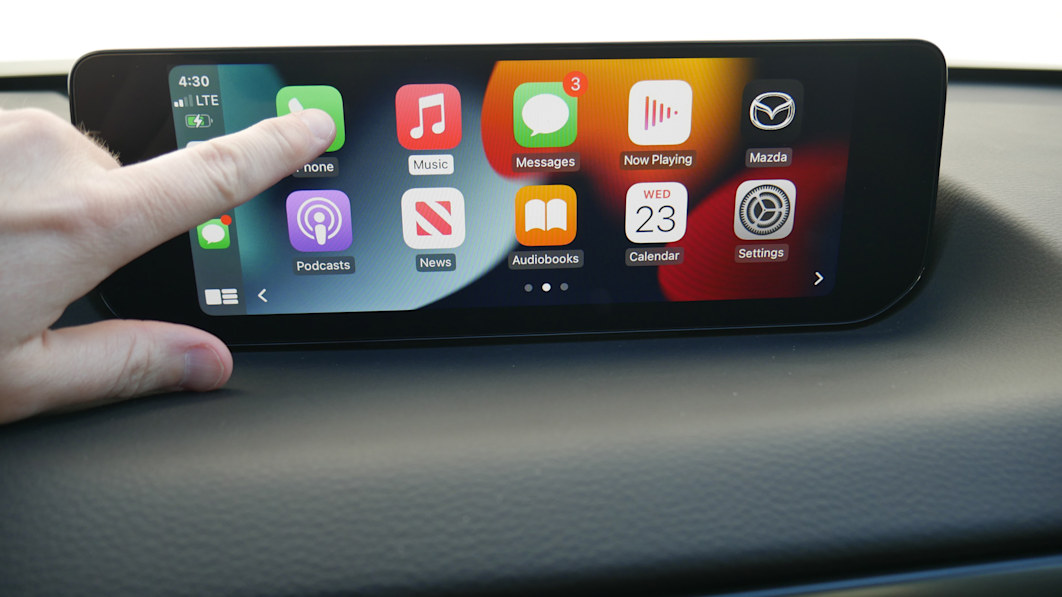
There’s a good reason Apple CarPlay and Google’s Android Auto drive the nail in the coffin of automakers’ own smartphone platforms: they work. Prior to the rollout of the platforms, automakers struggled to combine their in-car touchscreens and infotainment systems with buttons and displays with smartphones. Such media player interfaces were and still are confusing, frustrating or glitchy.
Enter CarPlay and Android Auto, which use software to largely mirror what’s on a driver’s device — in a sleek and relatively safe car-centric manner — onto a car’s infotainment screen. They encompass the apps and interfaces that owners of the devices already know and appear the same on every in-dash display – be it in a Bentley or a Buick.
What type of phone do you need for Apple CarPlay and Android Auto?
CarPlay is now compatible with the iPhone 5, without the need for a separate app. Android Auto, on the other hand, requires downloading an app for devices running Android 9 or below, while devices running Android 10 and above do not require a separate app.
What apps are available for Android Auto and Apple CarPlay?
Both platforms include native apps for familiar features such as calling, messaging, music, maps, audiobooks, and podcasts, and leverage the parent company’s voice assistant for hands-free functionality. They also integrate popular third-party apps for music streaming, messaging, navigation, parking, shopping, sports, and even electric vehicle charging.
More than 600 vehicle models now offer CarPlay and more than 500 are now compatible with Android Auto. The platforms are also available in aftermarket head units, and in 2018 Mazda added CarPlay support to vehicles from the 2014 model year through a dealer-installed upgrade for vehicles equipped with the Mazda Connect system.
Some automakers were initially, and until recently, reluctant to allow Apple and Google in their dashboards. Toyota, in particular, objected to the automatic sharing of owner’s usage data with Apple and Google. At the time of writing, Tesla is the only major automaker to have eschewed the platforms and stick to its own system.
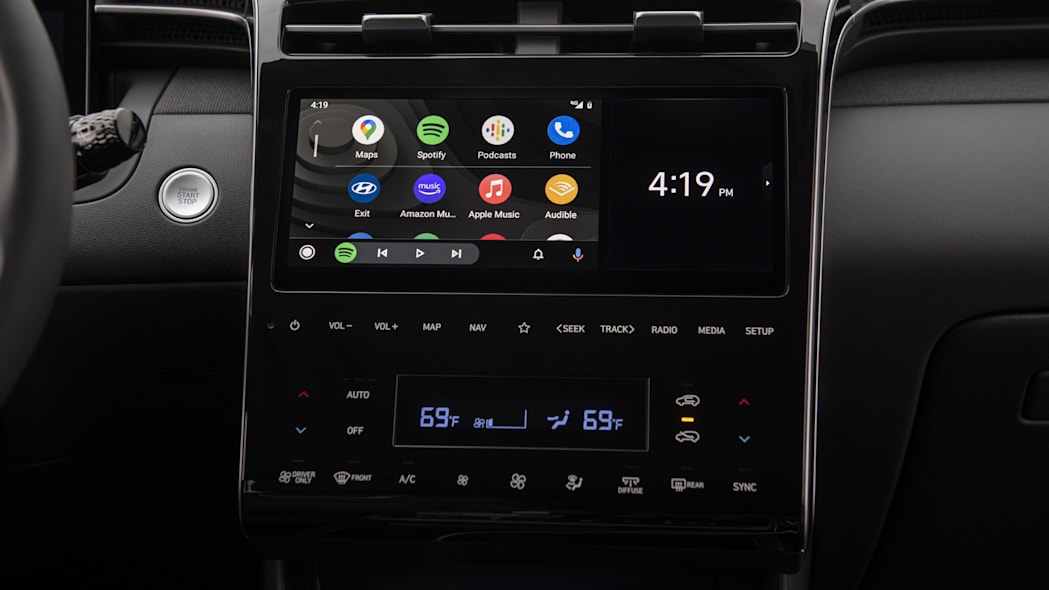

What is the difference between wired and wireless Apple CarPlay and Android Auto?
In most cases, a device must be connected to the USB port with smartphone integration in the car. (This port may be labeled as such or with a white border in your car.) But with the release of iOS 9 in September 2015, more than 20 carmakers now offer wireless CarPlay, while Android had already cut the cord by March 2015. (A handful of automakers only offer wireless CarPlay.)
Wireless CarPlay and Android Auto cannot use a Bluetooth connection and instead require connection to a vehicle via Wi-Fi. No, this doesn’t mean they’re chewing through the data cap for an in-car Wi-Fi hotspot. Because the platforms are data-intensive, they need this more robust connection to the car’s infotainment system.
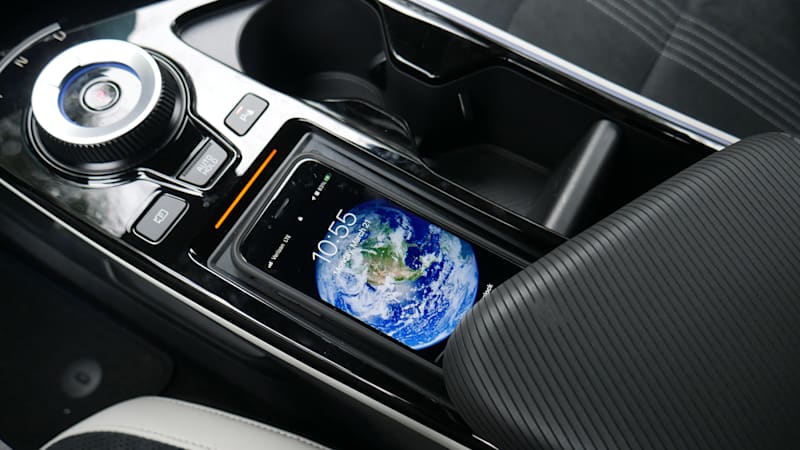
A disadvantage of wireless Apple CarPlay and Android Auto is that a Wi-Fi connection drains a device’s battery faster. Of course, you can always plug the device into a charging-only USB port, and if your car is equipped with wireless charging and wireless CarPlay and Android Auto, you get the best of both worlds.


Will Apple CarPlay and Android Auto be updated?
Besides their simplicity and familiarity, one of the biggest advantages of CarPlay and Android Auto over the smartphone integration platforms of car manufacturers is that they are regularly refreshed via software updates. While a handful of automakers offer over-the-air software updates for their infotainment systems, it’s not that simple and seamless for anyone but Tesla to update your smartphone while you sleep, and get new and improved features.
In addition to adding wireless capabilities, the iOS 9 update allowed car companies to develop apps that allow car occupants to control vehicle-specific functions such as climate controls. Subsequent updates added features such as support for third-party navigation apps like Waze and food ordering and parking apps.
With the release of iOS 13 in 2019 came one of the biggest changes to CarPlay: a Dashboard feature with a split screen option that can simultaneously display maps, media information, and calendar items. It has also added a Settings app that allows users to switch between light and dark modes, customize album art in the Now Playing screen, and enable a Do Not Disturb feature.
Last year, for certain 2021 models, CarPlay added the ability to unlock a car and start the engine with an iPhone. The feature also makes it possible to share digital “keys” with family or friends and even works for up to five hours after an iPhone’s battery runs out.
Android Auto is also consistently updated. Google initially did not allow third-party map apps to integrate with Android Auto, reserving the platform for its own Google Maps and Waze. But now third-party map apps are available, such as Sygic and TomTom AmiGO.
In late 2016, Google added the ability to run Android Auto as an app on an Android device. In this case, that means via a built-in Android Automotive OS, which so far has been run by only a few vehicles, most notably Polestar EVs.
In early 2018, Google announced the addition of Google Assistant to Android Auto, while in July 2019 the platform received a UI overhaul. Last summer, Android Auto received a major upgrade that made it possible to personalize the home screen directly from your phone, an AZ fast scroll function for long catalogs of numbers and contact list, and integration of EV charging, parking and navigation apps.
What limitations do Apple CarPlay and Android Auto have?
Neither system is a complete replacement for a car’s native infotainment system. If you want to listen to the radio, be it terrestrial or SiriusXM, you need the interface of the car. Same if you want to change different vehicle functions. Navigation apps like Google Maps also rely on data to be able to find a new destination and map out a route – if you’re in an area with no service and don’t have pre-downloaded map data (most people don’t know once you know you can do that), you don’t have a sat nav. That’s one of the reasons automakers continue to offer native navigation systems, although some, like new systems from Mercedes, offer augmented reality directions on the center screen or head-up display that you certainly won’t get with Google Maps.
What Apple CarPlay can or cannot do also depends on the car. Some block CarPlay’s ability to look through playlists in the music app while the car is in motion, such as selecting something with Siri. Others, however, keep everything available to you all the time.
What is the difference between Android Auto and Android Automotive OS?
We’ve already described Android Auto, but you’re going to see the term Android Automotive more and more, which isn’t the same. Rather than just providing an interface to control your smartphone through the car’s infotainment system, Android Automotive is in fact the entire infotainment system. It’s basically an operating system created by Google that car brands can customize with their specific designs or “skins” that can control everything a car’s original system would normally do. So think of changing a radio station or adjusting the settings of the driving mode. Android Auto is still required to communicate and operate smartphone apps, and while CarPlay was not yet compatible at the time of writing, it will be in the future. You can see more below about Android Automotive and its early adoption in the 2022 GMC Yukon.
