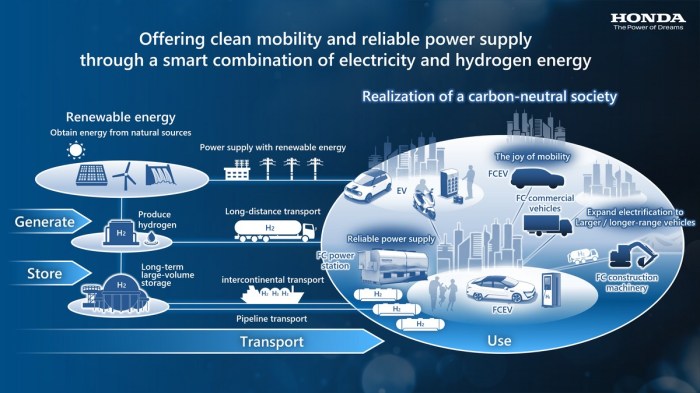
Honda General Motors hydrogen fuel cell production start – Honda General Motors has commenced production of hydrogen fuel cells, a significant milestone in the development of clean energy technology. This partnership between two automotive giants aims to accelerate the adoption of hydrogen fuel cells, offering a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
The production process involves advanced technologies that harness the power of hydrogen to generate electricity, with minimal emissions. The fuel cells are designed for various applications, including transportation, power generation, and industrial uses.
Market Overview

The hydrogen fuel cell production market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by increasing concerns over climate change and the need for clean energy sources. In 2022, the global market size was valued at USD 1.2 billion and is projected to reach USD 12.9 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 35.6% during the forecast period.
The market is highly competitive, with major players such as Toyota, Hyundai, and Honda investing heavily in research and development. Key trends shaping the market include the development of more efficient and affordable fuel cells, the expansion of hydrogen refueling infrastructure, and the growing adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
Key Players
The global hydrogen fuel cell production market is dominated by a few key players, including:
- Toyota
- Hyundai
- Honda
- Ballard Power Systems
- Plug Power
Honda and General Motors Partnership: Honda General Motors Hydrogen Fuel Cell Production Start
In 2021, Honda and General Motors (GM) formed a strategic partnership to advance the development and production of hydrogen fuel cell systems for heavy-duty trucks. The partnership aims to accelerate the commercialization of zero-emission fuel cell technology in the transportation sector.
Goals and Objectives
- Develop a next-generation hydrogen fuel cell system that is more efficient, durable, and cost-effective than current systems.
- Establish a joint manufacturing facility to produce the fuel cell systems for heavy-duty trucks.
- Work together to promote the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology in the commercial trucking industry.
Timeline
The partnership is expected to have the following timeline:
- 2021: Announcement of the partnership and establishment of a joint venture.
- 2023: Completion of the joint manufacturing facility.
- 2024: Start of production of the next-generation hydrogen fuel cell system.
Roles and Responsibilities
Honda and GM will have the following roles and responsibilities in the partnership:
- Honda:Provide its expertise in fuel cell technology development and manufacturing.
- GM:Provide its expertise in heavy-duty truck engineering and manufacturing, as well as its sales and distribution network.
Production Process and Technology
The production of hydrogen fuel cells involves several key steps and technologies.
The first step is the production of the membrane electrode assembly (MEA), which is the core component of the fuel cell. The MEA is made by coating a thin layer of platinum or other catalyst onto a polymer membrane. The membrane allows hydrogen ions to pass through, while the catalyst helps to split hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons.
Stack Assembly
The next step is to assemble the MEA into a stack. A stack is made up of multiple MEAs that are connected in series. The stack is then placed in a housing, which protects it from the environment and provides the necessary electrical connections.
Fuel Supply and Management
The fuel cell also requires a supply of hydrogen fuel. The hydrogen is typically stored in a tank and then supplied to the fuel cell through a series of valves and pipes. The fuel cell then uses the hydrogen to produce electricity.
Challenges and Opportunities in Scaling Up Production
There are a number of challenges associated with scaling up the production of hydrogen fuel cells. One challenge is the cost of the materials used in the fuel cell. Platinum is a particularly expensive material, and the cost of the MEA can be a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cells.
Another challenge is the need to develop more efficient manufacturing processes. The current production process for hydrogen fuel cells is relatively labor-intensive, and it can be difficult to scale up production without increasing costs.
Despite these challenges, there are also a number of opportunities for scaling up the production of hydrogen fuel cells. One opportunity is the development of new materials that are less expensive than platinum. Another opportunity is the development of new manufacturing processes that are more efficient and cost-effective.
Applications and Use Cases

Hydrogen fuel cells possess a wide range of potential applications, offering a clean and efficient energy solution for various industries and sectors.
One of the primary applications of hydrogen fuel cells lies in the transportation sector. They can power vehicles, such as cars, buses, and trucks, without producing tailpipe emissions. Hydrogen-powered vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality, contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
Automotive Industry
- Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) offer zero-emission driving, with water vapor as the only byproduct.
- Hydrogen refueling stations are being developed to support the growing demand for FCEVs.
Industrial Applications, Honda General Motors hydrogen fuel cell production start
- Hydrogen fuel cells can provide backup power for critical infrastructure, such as hospitals and data centers.
- They can be used in portable power generators for remote areas or disaster relief situations.
Residential and Commercial Buildings
- Hydrogen fuel cells can generate electricity and heat for homes and businesses, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- They offer a clean and efficient alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems.
While hydrogen fuel cells offer significant benefits, it’s important to note their limitations. One challenge lies in the production and storage of hydrogen. Hydrogen is a gas and requires specialized infrastructure for transportation and storage. Additionally, the cost of hydrogen fuel cells and the availability of hydrogen refueling stations need to be addressed for widespread adoption.
Environmental Impact
Hydrogen fuel cells have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. They produce only water vapor as a byproduct, making them a clean and sustainable source of energy.
Compared to other alternative energy sources, hydrogen fuel cells offer several advantages. They have a higher energy density than batteries, meaning they can store more energy in a smaller space. They also have a longer range than electric vehicles, and refueling is faster than charging an electric battery.
Potential for Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The potential for hydrogen fuel cells to reduce greenhouse gas emissions is significant. A study by the International Energy Agency found that hydrogen fuel cells could reduce global CO2 emissions by up to 30% by 2050. This would be a major step towards achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius.
Economic Considerations

Evaluating the economic feasibility of hydrogen fuel cell production involves considering costs associated with production, infrastructure, and maintenance. The potential return on investment (ROI) for companies investing in this technology is also crucial.
Notice Nissan IMX concept will reportedly influence next-gen rogue sport for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Costs
- Production costs:Establishing and operating hydrogen fuel cell production facilities require significant capital investment. Costs include raw materials, manufacturing equipment, and labor.
- Infrastructure costs:Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs) require dedicated fueling stations. Building and maintaining these stations involves substantial infrastructure investment.
- Maintenance costs:Like any vehicle, FCEVs require regular maintenance, including servicing the fuel cell stack, which can be more complex and expensive than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Return on Investment
The ROI for hydrogen fuel cell technology depends on various factors, including government incentives, market demand, and technological advancements. Companies investing in this technology aim to capitalize on potential long-term benefits such as reduced emissions, increased energy efficiency, and the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions.
Future Outlook

The future of hydrogen fuel cell production looks promising, with several factors driving its growth. Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the potential of hydrogen as a clean and sustainable energy source, leading to supportive policies and regulations. Moreover, technological advancements are reducing production costs and improving the efficiency of fuel cells, making them more competitive with traditional fossil fuels.
Growth Areas and Challenges
Key growth areas for hydrogen fuel cell production include transportation, power generation, and industrial applications. In transportation, hydrogen fuel cells are expected to play a significant role in reducing emissions from heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks and buses. In power generation, fuel cells offer a reliable and efficient alternative to fossil fuels, especially in remote areas or during peak demand periods.
In industries, hydrogen fuel cells can provide clean and sustainable power for various processes, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving energy efficiency.Despite the potential, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cells. These include the high cost of production, the need for a robust hydrogen infrastructure, and concerns about the safety of hydrogen storage and transportation.
Role of Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the future of hydrogen fuel cells. Supportive policies, such as tax incentives, funding for research and development, and mandates for clean energy adoption, can accelerate the growth of the industry.
Additionally, regulations related to hydrogen safety, transportation, and infrastructure development are essential to ensure the safe and responsible use of hydrogen fuel cells.
Final Review

Honda General Motors’ hydrogen fuel cell production is a testament to the growing momentum behind clean energy solutions. As the demand for sustainable technologies increases, hydrogen fuel cells are poised to play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning towards a greener future.